PALS Tachycardia Initial Management Algorithm
1. Tachycardia is diagnosed by manual testing or heart rate monitor– Normal heart rates vary with age/size.
| Age Category | Age Range | Normal Heart Rate |
| Newborn | 0-3 months | 80-205 per minute |
| Infant/Young child | 4 months to 2 years | 75-190 per minute |
| Child/School Age | 2-10 years | 60-140 per minute |
| Older child/ Adolescent | Over 10 years | 50-100 per minute |
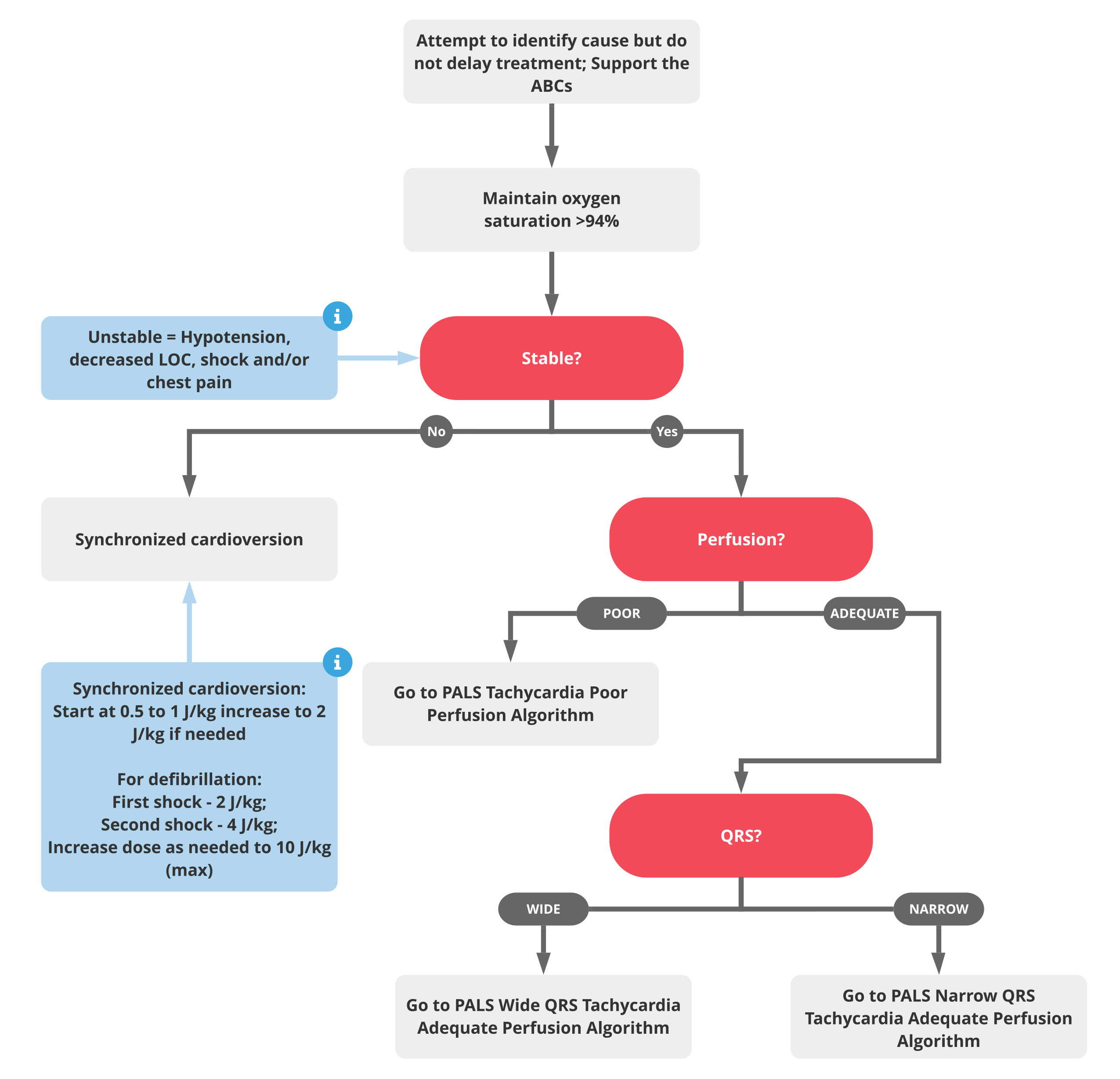
2. Consider possible causes but do not delay treatment
- Vagal Maneuvers
- Synchronized Cardioversion
- Medications
- Support Airway, Breathing, Circulation
3. Is the child stable or unstable?
A child with tachycardia is considered unstable if he or she is hypotensive, has a decreased level of consciousness, is in shock, or is experiencing ischemic chest pain.
Unstable child – administer synchronized cardioversion immediately
For synchronized cardioversion, begin with an electrical dose of 0.5 to 1 J/kg of the child’s body weight. If ineffective, increase the energy level to 2 J/kg. For defibrillation (cardiac arrest with a shockable rhythm), first shock should be given at 2 J/kg and the second shock should be given at 4 J/kg. Subsequent shocks may be higher, up to the adult maximum of 10 J/kg body weight.
Stable child – continue assessment
| Age Category | Age Range | Systolic Blood Pressure | Diastolic Blood Pressure | Abnormally Low
Systolic Pressure |
| Neonate | 1 Day | 60-76 | 30-45 | <60 |
| Neonate | 4 Days | 67-84 | 35-53 | <60 |
| Infant | To 1 month | 73-94 | 36-56 | <70 |
| Infant | 1-3 months | 78-103 | 44-65 | <70 |
| Infant | 4-6 months | 82-105 | 46-68 | <70 |
| Infant | 7-12 months | 67-104 | 20-60 | <70 + (age in years x 2) |
| PreSchool | 2-6 years | 70-106 | 25-65 | <70 + (age in years x 2) |
| School Age | 7-14 years | 79-115 | 38-78 | <70 + (age in years x 2) |
| Adolescent | 15-18 years | 93-131 | 45-85 | <90 |
4. Assess the child’s tissue perfusion
If tissue perfusion is poor, move directly to the PALS Tachycardia Poor Perfusion Algorithm
If tissue perfusion is adequate…
5. Measure the width of the child’s QRS complex on ECG
If the QRS complex is narrow (QRS ≤0.09 sec), move to the PALS Narrow QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm
If the QRS complex is wide (QRS >0.09 sec), move to the PALS Wide QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm