ACLS Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm
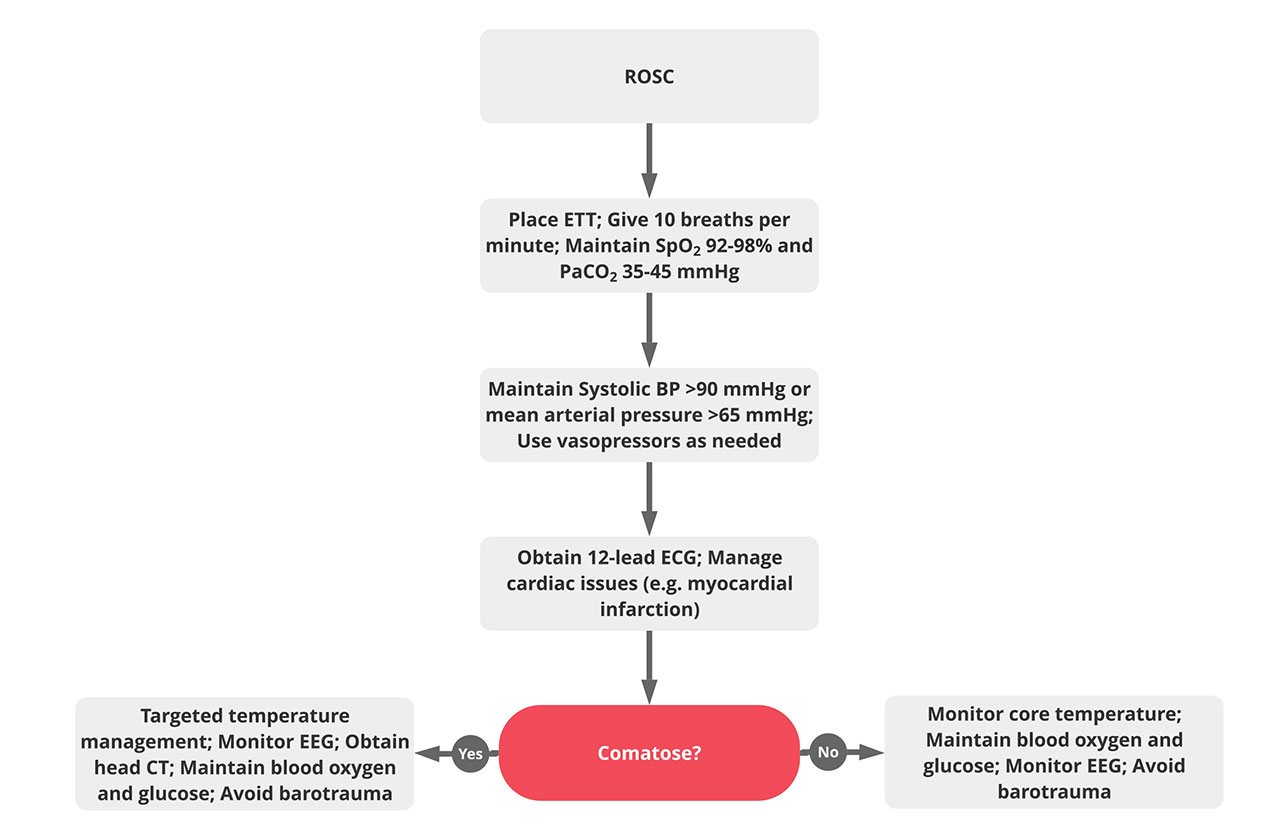
Treatment for a victim of cardiac arrest must continue post resuscitation in order to optimize the outcomes. The post cardiac arrest care algorithm includes the following steps:
- Verify ROSC.
- Manage the airway including ETT placement and provide 10 breaths per minute.
- Using quantitative waveform capnography, titrate the oxygen to maintain a PETCO2 of 35-40 mm Hg. If you do not have access to a waveform capnography machine, titrate oxygen to keep the oxygen saturation 92% to 98%.
- Insert and maintain an IV for medication administration. Maintain systolic blood pressure above 90 mm Hg and/or mean arterial pressure above 65 mm Hg. For a low blood pressure, consider one or more of these treatments:
- Give 1 to 2 liters of saline or Ringer’s lactate IV fluid.
- Start an epinephrine IV or a dopamine IV infusion
- Consider norepinephrine for extremely low systolic blood pressure.
- Obtain a 12-lead ECG and rule out myocardial infarction. If myocardial infarction is suspected, consider percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) to open the coronary arteries.
- Determine if the patient is comatose.
- If comatose:
- Targeted temperature management ASAP keeping body temp 32-36°C for 24 hours initially.
- Monitor EEG and assess for nonconvulsive seizures (treat if present)
- Obtain head CT
- Maintain oxygen, glucose, carbon dioxide, etc.
- Avoid barotrauma
- If NOT comatose (awake):
- Maintain oxygen, glucose, carbon dioxide, etc.
- Avoid barotrauma
- If comatose: